ද්වාරය:නැගෙනහිර ආසියාවේ භාෂා හා සාහිත්ය

Altaic languages
[edit]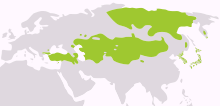
Altaic is a proposed language family that is held by its proponents to include the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, and possibly the Japonic language families and the Korean language isolate. These languages are spoken in a wide arc stretching from northeast Asia through Central Asia to Anatolia and eastern Europe (Turks, Kalmyks). The group is named after the Altai Mountains, a mountain range in Central Asia.Template:Wikipediaref
තුර්කි
[edit]Manchu
[edit]Ainu
[edit]ජපන්
[edit]- See also Japanese Wikisource
Japanese is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic (or Japanese-Ryukyuan) language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists.Template:Wikipediaref
භාෂාව
[edit]සාහිත්යය
[edit]- A History of Japanese Literature, 1909 by William George Aston
- Kimi ga Yo, Japanese national anthem, lyrics based on a waka poem written in the Heian period (794-1185), 1880 melody by Yoshiisa Oku and Akimori Hayashi, supervised by Hiromori Hayashi (partly based on the original 1870 melody by John William Fenton)
- Botchan, 1906 novel by Natsume Sōseki, translated by Yasotaro Morri
- Rashōmon, 1914 by Ryūnosuke Akutagawa
කොරියන්
[edit]- See also Korean Wikisource
Korean is the official language of Korea, both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing system was commissioned by Sejong the Great, the system being currently called Hangul.Template:Wikipediaref
- Baekbeomilji, 1947 by Kim Gu, translated by Wikisource
චීන
[edit]- See also Chinese Wikisource and Min Nan Wikisource
Chinese, or the Sinitic language(s), is a language family consisting of languages which are mostly mutually unintelligible to varying degrees. There are between 7 and 13 main regional groups of Chinese (depending on classification scheme), of which the most spoken, by far, is Mandarin (about 850 million), followed by Wu (90 million), Cantonese (Yue) (70 million) and Min (50 million). Most of these groups are mutually unintelligible, although some, like Xiang and the Southwest Mandarin dialects, may share common terms and some degree of intelligibility.Template:Wikipediaref
භාෂාව
[edit]- Chinese Without a Teacher, 1922 by Herbert Allen Giles
- Essays on the Chinese Language, 1889 by Thomas Watters
- A progressive course of colloquial Chinese, 1903 by Thomas Francis Wade
- Chinese Dialogues, Questions, and Familiar Sentences, Literally Rendered (1863), by Walter Henry Medhurst (1796-1857), revised by Walter Henry Medhurst (1822-1885) (start transcription)
- Synoptical Studies in Chinese Character, 1874 by Herbert Allen Giles
- The Chinese Speaker. Readings in Modern Mandarin, 1916 by Evan Morgan
- Template:Article link
Cantonese
[edit]Chaozhou
[edit]- A Chinese and English vocabulary, in the Tie-chiu dialect (start transcription), 1883 by Josiah Goddard
- First Lessons in the Tie-chiw Dialect (start transcription), 1841 by William Dean
Fuzhou
[edit]- The Chinese Language Spoken at Fuh Chau, 1856 by Moses Clark White
- Dictionary of the Foochow Dialect, 1929 by R. S. Maclay, C. C. Baldwin and Samuel H. Leger
- An English-Chinese Dictionary of the Foochow Dialect (start transcription), 1905 by T. B. Adam
- A Manual of the Foochow Dialect In Twenty Lessons (start transcription), by C. M. S. and A. E. Champness
Shantou
[edit]- English-Chinese Vocabulary of the Vernacular Or Spoken Language of Swatow (start transcription), 1883 by Rudolf Lechler, Samuel Wells Williams, William Duffus
- Handbook of the Swatow Vernacular (start transcription), 1886 by Lim Hiong Seng
- Dictionary of the Swatow dialect, 1883 by Adele Marion Fielde
සාහිත්යය
[edit]- See Portal:චීන සාහිත්යය
- See also Portal:Chinese classics
බුරුම
[edit]The Burmese language is the official language of Burma. Burmese is the native language of the Bamar and related sub-ethnic groups of the Bamar, as well as that of some ethnic minorities in Burma like the Mon.Template:Wikipediaref
- Grammatical Notices of the Burmese Language, 1842 by Adoniram Judson
- Grammar of the Burmese Language, 1883 by Adoniram Judson
තායි
[edit]- වැඩිදුර තොරතුරු සඳහා Portal:තායි භාෂාව
- See also තායි විකිමූලාශ්ර
ද්රවිඩ භාෂා
[edit]The Dravidian languages are a language family spoken mainly in southern India and parts of eastern and central India as well as in northeastern Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, and overseas in other countries such as Malaysia and Singapore. The most populous Dravidian languages are Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam.Template:Wikipediaref
- වැඩිදුර තොරතුරු සඳහා Portal:ද්රවිඩ භාෂා සහ සාහිත්යය
සිංහල
[edit]- වැඩිදුර තොරතුරු සඳහා Portal:සිංහල භාෂාව
